OSPF
Introduction
OSPF uses SPF to find the shortest path to the destination. In other to do that, OSPF routers need to understand the full topology of the network. It's not scalable to use all information in the network because it will generate too many informations. OSPF introduces 7 LSAs to depict the full topology.
OSPF routes have an AD of 110
OSPF uses IP protocol 89, not TCP or UDP
The dead timer is 4x the Hello interval
Adjacency Requirements
- Same area
- Authentication match
- Subnet mask match
- Hello and dead timers match
- Stub flags match
- MTU match
State
- Down
- Attempt
- Init
- 2-Way
- Exstart
- Exchange
- Loading
- Full
Metric Calculation
(config)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth <bandwidth in Mbps>
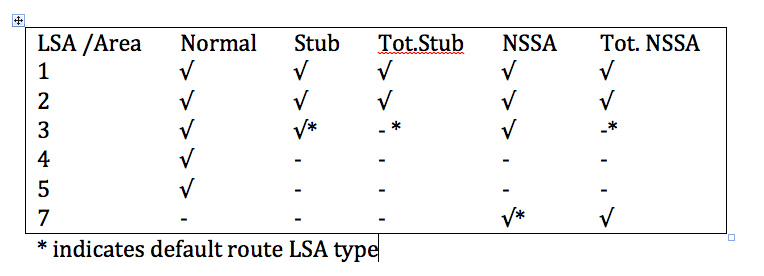
LSA
There are 6 LSA types:
http://blog.xuite.net/juilin77/happy/5702604-OSPF+LSA+Types%E6%95%B4%E7%90%86
Network Area
There are 6 area types in OSPF:
- Backbone area (area 0)
- Standard area
- Stub area
- Totally stubby area
- Not-so-stubby area (NSSA)
- Totally Not-so-stubby area
Network Type
Stub network is serial link(point to point), loopback
Transit network is Ethernet link(multi-access?)
Route Summarization
Since OSPF is a link state routing protocol, it is impossible to filter or summarize the routes in any router. Instead, the summarization need to be applied in the ABR or ASBR and advertised via a network summary LSA(Type 3 LSA).
on ABR
R1(config-router)# area 18 range 8.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
This will summarize the subnet of 8.0.0.0/8 into only 1 summary route.
Typically set on ABR for summarizing the routes that are added using network command.
This summary route will not be advertised if there is no subnet of 8.0.0.0/8 exists in R1's routing table.
on ASBR
R1(config-router)# summary-address 1.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
This will summarize the subnet of 1.0.0.0/8 into only 1 summary route.
Typically set on ASBR for summarizing the redistributed routes.
This summary route will not be advertised if there is no subnet of 1.0.0.0/8 exists in R1's routing table.